Zero-Shot Unsupervised and Text-Based Audio Editing Using DDPM Inversion
ICML 2024
Technion - Israel Institute of Technology
Abstract
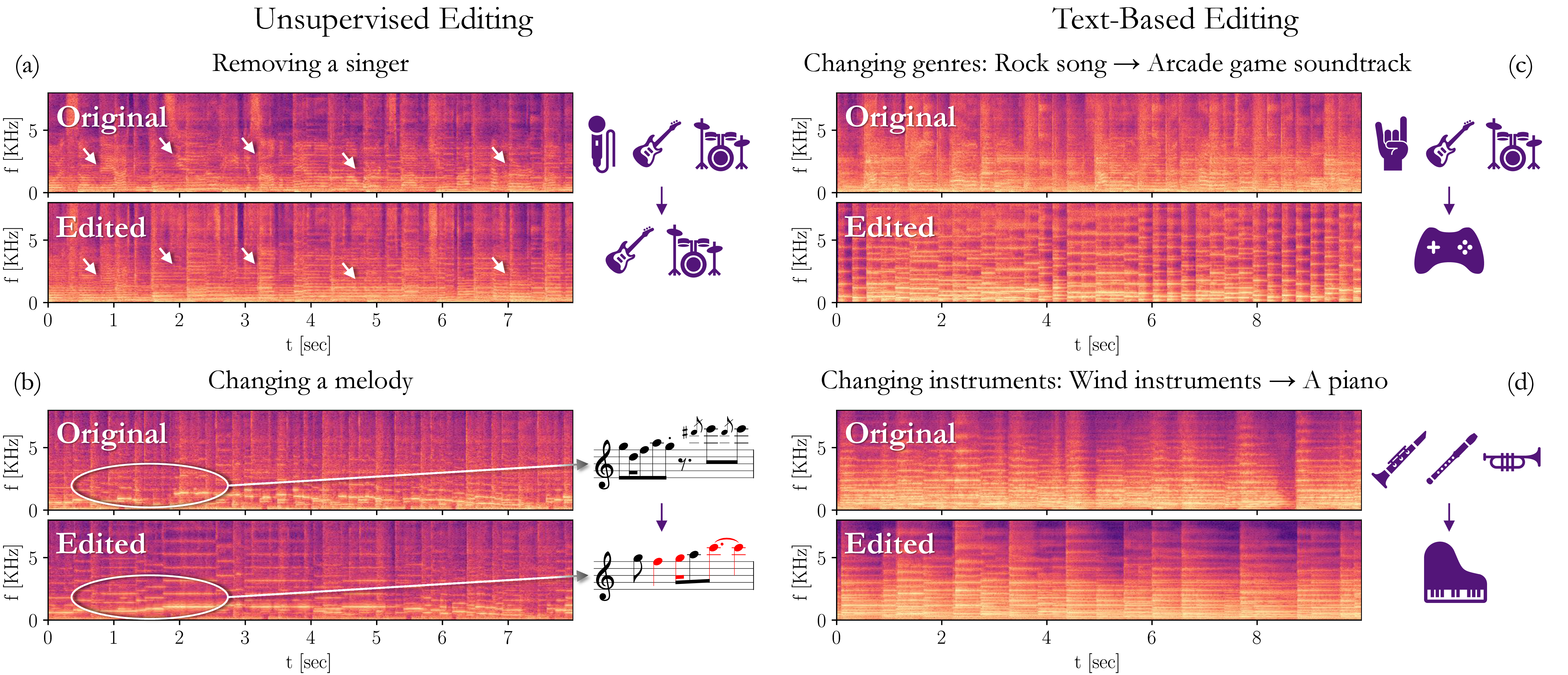
Editing signals using large pre-trained models, in a zero-shot manner, has recently seen rapid advancements in the image domain. However, this wave has yet to reach the audio domain. In this paper, we explore two zero-shot editing techniques for audio signals, which use DDPM inversion on pre-trained diffusion models. The first, adopted from the image domain, allows text-based editing. The second, is a novel approach for discovering semantically meaningful editing directions without supervision. When applied to music signals, this method exposes a range of musically interesting modifications, from controlling the participation of specific instruments to improvisations on the melody.
Video Overview
For people in a hurry. Images were generated by DALL-E 2 and Copilot.
1. Samples of Editing
1.1. Samples of Text-Based Editing
| # | Source Prompt | Target Prompt | Original Audio | Edited Audio | Edit Tstart |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A recording of a sneaky jazz song. | A recording of a tense classical music score. | 110 | ||
| 2 | A recording of a hard rock song. | A recording of a jazz song. | 100 | ||
| 3 | A recording of a happy upbeat classical music piece. | A recording of a happy upbeat arcade game soundtrack. | 100 | ||
| 4 | Trumpets playing alongside a piano, bass and drums in an upbeat old-timey cool jazz song. | A banjo playing alongside a piano, bass and drums in an upbeat old-timey cool country song. | 90 | ||
| 5 | —— | A recording of a dark techno song. | 90 | ||
| 6 | A recording of a dramatic epic Chinese piece. | A recording of a dramatic heavy metal piece. | 40 | ||
| 7 | A recording of a rock song. | A recording of Arabic music. | 110 | ||
| 8 | —— | A recording of a funky hip hop song. | 110 | ||
| 9 | A high quality recording of wind instruments and strings playing. | A high quality recording of a piano playing. | 70 | ||
| 10 | A recording of an upbeat gospel song. | A recording of an upbeat techno song. | 100 | ||
| 11 | A recording of a happy upbeat song in a Latin jazz style. | A recording of a happy upbeat song in a retro arcade game soundtrack style. | 90 | ||
| 12 | —— | A recording of an upbeat cool jazz song. | 90 | ||
| 13 | A recording of an old rock song. | A recording of an techno song. | 90 | ||
| 14 | Chinese strings, flutes, and harps playing an upbeat piece. | Chinese strings, flutes, and harps playing an somber piece. | 80 | ||
| 15 | —— | A recording of an upbeat arcade game soundtrack. | 80 | ||
| 16 | A high quality recording of a cat meowing. | A high quality recording of a dog barking. | 150 | ||
| 17 | A high quality recording of a dog barking a lot. | A high quality recording of a gun shooting a lot. | 100 | ||
| 18 | A kid talking loudly. | A rooster crowing. | 110 | ||
1.2. Samples of Unsupervised Editing
For the unsupervised editing, we split the samples into two sections.The first section (Strength changes) shows how the same direction applied with different strengths changes the audio sequentially.
The second section (PC direction changes) shows how removing or adding a direction removes or adds a concept.
1.2.1. Various Samples (Strength changes)
| # | Inversion Prompt | Original Audio | Edited Audio +PC | Edited Audio +2PC | PC Interpretation | Edit Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A high quality recording of flutes and a trumpet playing. | Melody change | t'∈[200, -1] Specific t=80 used PCs 1+2+3 |
|||
| 2 | A recording of a calm country song. | Remove singer | t'∈[150, -1] Specific t=115 used PCs 1+2+3 |
|||
| 3 | — | Just drums | t'∈[150, -1] Specific t=80 used PCs 1+2+3 |
|||
| 4 | A recording of a scary classical music piece. | Melody change | t'∈[150, 50] Specific t=95 used PCs 1+2+3 |
|||
| 5 | A trumpet and a saxophone playing a cool jazz melody, with an accompaniment of a piano, bass and drums. | Melody change | t'∈[135, 95] PCs 1+2+3 |
|||
| 6 | A high quality recording of wind instruments and strings playing. | Melody change | t'∈[135, 95] PCs 1+2+3 |
|||
| 7 | A strings section playing classical music. | Minor melody changes | t'∈[95, 80] PCs 1+2+3 |
|||
| 8 | A high quality recording of a woman singing while a guitar and drums play in the background. | Instrument change | t'∈[200, -1] Specific t=65 used PCs 1+2+3 |
|||
| 9 | A high quality recording of wind instruments and strings playing. | Melody changes | t'∈[200, -1] Specific t=135 used PC #3 |
|||
| 10 | A high quality recording of a rock band playing an upbeat rock song. | Drums style change | t'∈[200, -1] Specific t=95 used PCs 1+3 |
|||
1.2.2. Various Samples (PC direction changes)
| # | Inversion Prompt | Edited Audio -γPC | Original Audio | Edited Audio +γPC | PC Interpretation | Edit Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A high quality recording of a man singing and drums, guitar and bass playing a song, and later a woman is singing. | Lead Guitar/Singers emphasis | t'∈[115, 80] PC #1 |
|||
| 2 | A high quality recording of a man singing and drums, guitar and bass playing a song, and later a woman is singing. | Singers/Drums emphasis | t'∈[115, 80] PC #2 |
|||
| 3 | A high quality recording of a man singing with a rock band accompaniment. | Drum-beats style | t'∈[200, -1] Specific t=80 used PC #1 |
|||
| 4 | A recording of ryhtmic clapping, a women singing, and drums and guitar playing. | Vibrato strength | t'∈[150, -1] Specific t=120 used PC #3 |
|||
| 5 | A recording of an old timey rock song from the sixties. | Guitar/Singer emphasis | t'∈[200, -1] Specific t=65 used PCs 1+2+3 |
|||
| 6 | — | Isolate Woman/Man | t'∈[115, 95] PC #1 |
|||
2. Comparisons to Other Methods
2.1. Comparisons of Text-Based Editing
2.1.2. Music Samples
| # | Source Prompt | Target Prompt | Original Audio | Ours | SDEdit Tstart=100 Tstart=70 Tstart=40 |
MusicGen | DDIM Inversion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A recording of a rock song. | A recording of Arabic music. |
Tstart=110 |
|
|||
| 2 | A recording of an upbeat rock song. | A recording of an arcade game soundtrack. |
Tstart=100 |
|
|||
| 3 | — | A recording of a dark techno song. |
Tstart=90 |
|
|||
| 4 | A high quality recording of wind instruments and strings playing. | A high quality recording of a piano playing. |
Tstart=70 |
|
|||
| 5 | — | A recording of an upbeat cool jazz song. |
Tstart=90 |
|
|||
| 6 | A recording of an old rock song. | A recording of an techno song. |
Tstart=90 |
|
|||
| 7 | A recording of a sneaky jazz song. | A recording of a tense classical music score. |
Tstart=110 |
|
|||
| 8 | — | A recording of a funky hip hop song. |
Tstart=110 |
|
|||
| 9 | — | A recording of an upbeat arcade game soundtrack. |
Tstart=80 |
|
|||
| 10 | A recording of an upbeat gospel song. | A recording of an upbeat techno song. |
Tstart=100 |
|
|||
| 11 | Trumpets playing alongside a piano, bass and drums in an upbeat old-timey cool jazz song. | A banjo playing alongside a piano, bass and drums in an upbeat old-timey cool country song. |
Tstart=90 |
|
|||
| 12 | A recording of a dramatic epic Chinese piece. | A recording of a dramatic heavy metal piece. |
Tstart=40 |
|
|||
| 13 | Chinese strings, flutes, and harps playing an upbeat piece. | Chinese strings, flutes, and harps playing an somber piece. |
Tstart=80 |
|
|||
| 14 | — | A recording of a happy arcade game soundtrack. |
Tstart=110 |
|
|||
| 15 | A recording of a hard rock song. | A recording of a jazz song. |
Tstart=100 |
|
|||
| 16 | A recording of a happy upbeat song in a Latin jazz style. | A recording of a happy upbeat song in a retro arcade game soundtrack style. |
Tstart=90 |
|
|||
2.1.2. Audio Samples
| # | Source Prompt | Target Prompt | Original Audio | Ours | SDEdit Tstart=150 | SDEdit Tstart=120 | SDEdit Tstart=100 | SDEdit Tstart=70 | DDIM Inversion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A high quality recording of a cat meowing. | A high quality recording of a dog barking. |
Tstart=150 |
||||||
| 2 | A high quality recording of a dog barking a lot. | A high quality recording of a gun shooting a lot. |
Tstart=100 |
||||||
| 3 | A kid talking loudly. | A rooster crowing. |
Tstart=110 |
2.2. Comparisons of Unsupervised Editing
| # | Inversion Prompt | Original Audio | Our Semantic Edit | SDEdit Tstart=115 | SDEdit Tstart=100 | SDEdit Tstart=85 | SDEdit Tstart=70 | Our Edit Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A high quality recording of a man singing and drums, guitar and bass playing a song, and later a woman is singing. | t'∈[115, 80] PC #1 |
||||||
| 2 | A high quality recording of a man singing with a rock band accompaniment. | t'∈[200, -1] Specific t=80 used PC #1 |
||||||
| 3 | — | t'∈[150, -1] Specific t=80 used PCs 1+2+3 |
||||||
| 4 | A high quality recording of flutes and a trumpet playing. | t'∈[200, -1] Specific t=80 used PCs 1+2+3 |
||||||
| 5 | A recording of a calm country song. | t'∈[150, -1] Specific t=115 used PCs 1+2+3 |
||||||
| 6 | A recording of a scary classical music piece. | t'∈[150, 50] Specific t=95 used PCs 1+2+3 |
||||||
| 7 | A trumpet and a saxophone playing a cool jazz melody, with an accompaniment of a piano, bass and drums. | t'∈[135, 95] PCs 1+2+3 |
||||||
| 8 | A high quality recording of wind instruments and strings playing. | t'∈[135, 95] PCs 1+2+3 |
||||||
| 9 | A strings section playing classical music. | t'∈[95, 80] PCs 1+2+3 |
||||||
| 10 | A recording of an old timey rock song from the sixties. | t'∈[200, -1] Specific t=65 used PCs 1+2+3 |
||||||
| 11 | A high quality recording of a woman singing while a guitar and drums play in the background. | t'∈[200, -1] Specific t=65 used PCs 1+2+3 |
||||||
Paper
Bibtex
More results and further discussion about our methods can be found in the supplementary material (included in the paper) and our supplemental examples page.
Acknowledgements
This webpage was originally made by Matan Kleiner with the
help of Hila Manor
for SinDDM and can be used as a template.
It is inspired by the template that was originally made by Phillip Isola and
Richard Zhang for a colorful ECCV project;
the code for the original template can be found here.
A lot of features are taken from bootstrap. All icons are taken from font awesome and
Academicons.

